Retargeting in Mobile User Acquisition: Definition, How It Works, and Best Practices
Introduction
In today’s highly competitive digital landscape, acquiring new users for a mobile app requires a significant investment. However, many users install an app without consistently engaging with it. This is where retargeting plays a crucial role in maximizing the value of acquired users.
Retargeting allows marketers to re-engage users who have installed an app but haven’t used it in a while, or encourage them to take specific actions (purchase, sign-up, subscription, etc.).
In this article, we’ll explore what retargeting is, how it works, and the best practices to achieve optimal results.
What is Retargeting and How Does It Work?
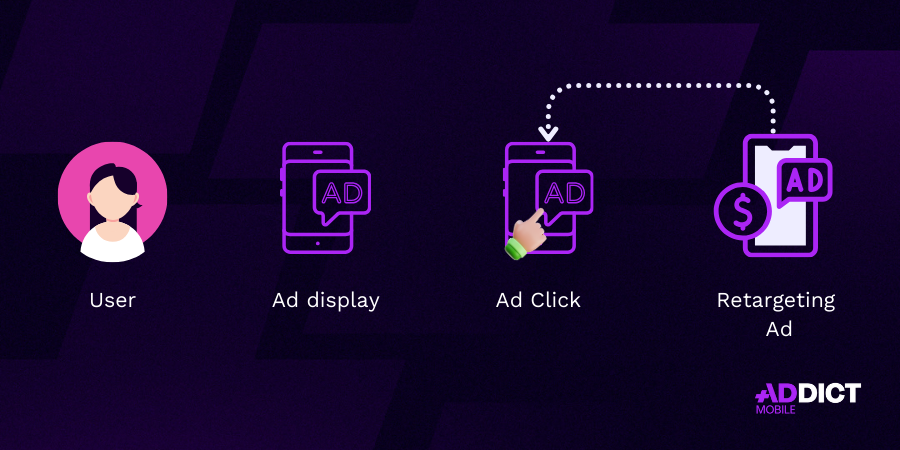
Retargeting, also known as ad retargeting, is a marketing strategy aimed at targeting users who have already interacted with an app (installation, browsing, incomplete actions) to encourage them to return and convert.
How Retargeting Works:
- Data Collection: The app gathers user behavior data through tracking tools (SDKs, MMPs like AppsFlyer, Adjust, etc.).
- Audience Segmentation: Users are categorized based on their activity (e.g., inactive for 7 days, abandoned carts, users who made a first purchase but not a second, etc.).
- Ad Delivery: Targeted ads are displayed across various channels (social ads, display, DSPs, mobile ad networks).
- Optimization and Iteration: Campaign performance is continuously analyzed to refine creatives and targeting strategies.
What Are the Different Types of Re-targeting?
Static vs. Dynamic Retargeting
- Static: Displays a generic ad to a predefined audience.
- Dynamic: Personalizes the ad based on user behavior (e.g., showing a product left in a shopping cart).
Retargeting Across Different Channels
- Social Media: Targeted ads on Facebook, Instagram, TikTok, etc.
- Display: Ads shown on websites and apps via Google Ads or DSPs.
- In-App: Push notifications, emails, and SMS to encourage users to return to the app.
- Search: Targeting users based on their searches on Google and other search engines.
Objectives and Benefits
Objectives
- Increase retention rates: Encourage users to return to the app.
- Improve conversion rates: Turn passive users into active customers.
- Maximize return on investment (ROI): Increase the value of already acquired users.
- Reduce churn: Decrease the number of users abandoning the app.
- Encourage high-value actions: Boost purchases, subscriptions, or user interactions.
Benefits
- Advanced personalization: Ads tailored to user behavior.
- Cost-effectiveness: More affordable than acquiring new users.
- Improved LTV (Lifetime Value): Increases long-term user value.
- Continuous optimization: Allows for real-time adjustments based on data.
Which Users Should You Target for Retargeting?
There are several user segments to focus on when implementing such a strategy:
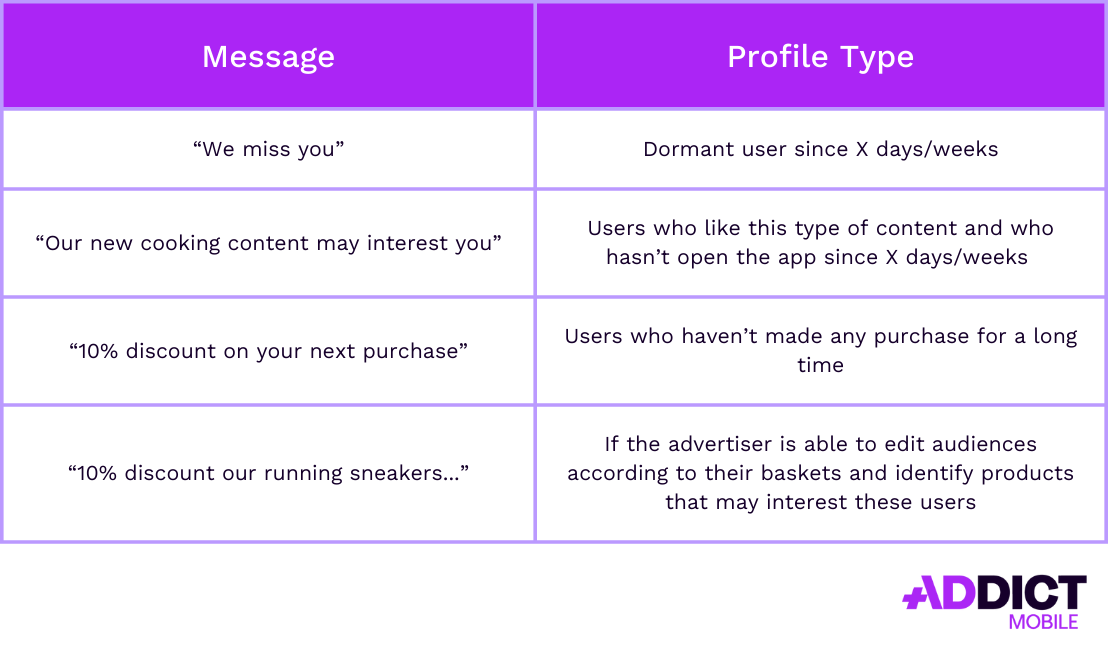
Dormant Users
A dormant user is someone who has installed an app but hasn’t used it for an extended period. The definition of “dormant” varies by industry—for example, in an e-commerce app, a user may be considered dormant after seven days of inactivity, whereas in a mobile game, this threshold could be as short as three days.
For each user profile, tailored messaging can improve effectiveness:
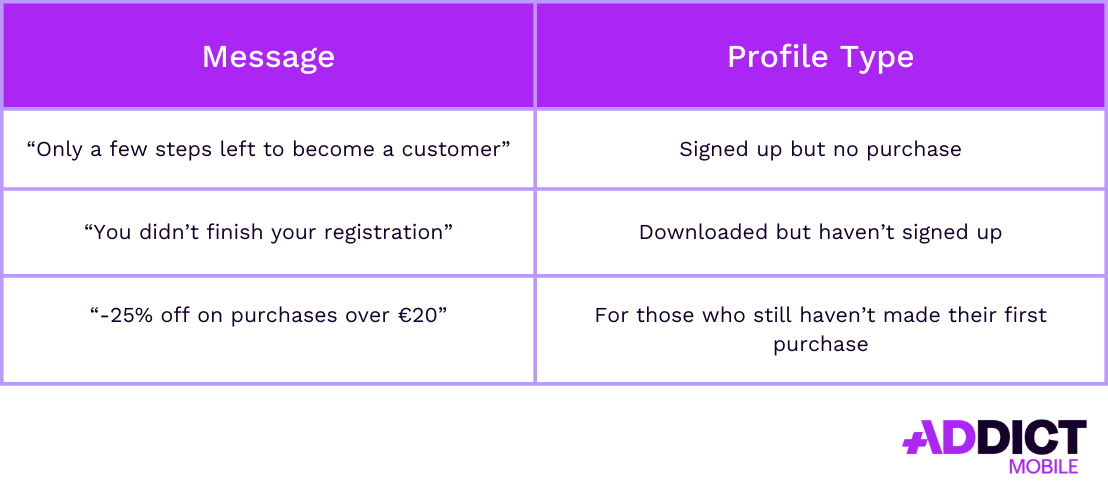
Unfinished Journeys
An unfinished journey user is someone who started an action within the app (sign-up, adding an item to the cart, beginning a game level) but didn’t complete it.
Within this category, three user profiles stand out:
- Registered users who haven’t made a purchase
- Users who downloaded the app but never signed up
- Users who have the app but haven’t made their first purchase
Going further :
👀 Check out our article: Retargeting : the keys for efficient campaigns
Re-targeting vs. Re-engagement: What’s the Difference?
- Retargeting: Uses paid ads to target users who have interacted with the app.
- Re-engagement: Encompasses all strategies (including push notifications and emails) aimed at bringing users back without ad spend.
Most advertisers take an omnichannel approach, effectively combining both methods to maximize performance.
How to Re-engage Users with Retargeting?
- Target Dormant Users Precisely: Identify inactivity periods and create specific segments (e.g., inactive for 7, 14, or 30 days).
- Offer Attractive Deals and Promotions: Provide discounts or exclusive perks to encourage users to return.
- Personalize Messaging: Use behavioral data to display relevant ads (e.g., highlighting a product viewed but not purchased).
- Leverage Multiple Channels: Implement a mixed approach that includes display ads, social media, and push notifications.
- Create a Sense of Urgency: Highlight limited-time offers to drive immediate action.
Best Practices for Effective Retargeting
- Refined Audience Segmentation: Tailor messaging based on user behavior.
- Optimized Timing: Find the right moment to serve ads.
- A/B Testing for Creatives: Test different ad variations to optimize engagement.
- AI-Powered Targeting: Use machine learning to predict behaviors and optimize bidding.
- Cross-Device Retargeting: Ensure a seamless experience across mobile, tablet, and desktop.
- Controlled Ad Frequency: Avoid ad fatigue and user rejection.
- Continuous Performance Analysis: Monitor KPIs and adjust strategies to improve results.
Going further:
👀 Check out our article on Creative Testing to optimize performance

Do not hesitate to contact with our teams
Addict can support you to improve your performance.
Key Concepts in Retargeting
- LTV (Lifetime Value): The total value a user generates throughout their engagement with the app. Retargeting helps increase this value by extending user activity.
- Churn Rate: The percentage of users who stop using an app. An effective retargeting campaign helps reduce churn.
- Audience Segmentation: The process of dividing users into homogeneous groups based on behavior to deliver more relevant ads.
- Mobile Attribution: Identifying which marketing channels contributed to a conversion—essential for measuring retargeting effectiveness.
- Dynamic Retargeting: A strategy that personalizes ads based on users’ past actions in the app.
- DSP (Demand-Side Platform): A platform that allows advertisers to buy ad impressions in real-time across multiple channels via programmatic bidding.
- IDFA & GAID: Unique identifiers for tracking users on iOS (IDFA) and Android (GAID). Their management directly impacts retargeting effectiveness, especially with Apple’s App Tracking Transparency (ATT) restrictions.
Conclusion
Retargeting is a powerful tool for mobile growth strategies. It helps maximize user engagement and optimize the return on investment of acquisition campaigns. Effective execution relies on smart segmentation, well-targeted ads, and continuous performance analysis.
With the rise of AI and machine learning technologies, retargeting will continue to evolve, offering increasingly advanced opportunities to boost retention and app monetization.


