Probabilistic Model in UA Attribution: Everything You Need to Know to Boost Your Advertising Campaigns
Introduction
Since Apple’s introduction of SKAN and the restrictions following the end of the IDFA, mobile acquisition has undergone a significant upheaval. These changes, centered on user privacy, have diminished marketers’ ability to directly track and attribute conversions to specific campaigns. The probabilistic model has emerged as a powerful alternative, leveraging trends and aggregated data to compensate for the loss of granular information. It provides marketers with a way to evaluate campaign impact while adhering to new regulations.
This article delves into the essence of the probabilistic model, why it is becoming central in UA, its advantages and limitations, and the contexts where it proves most relevant.

Probabilistic Model: A New Method for Ad Attribution
The probabilistic model uses advanced statistical methods to attribute user actions (such as an install or a purchase) to a specific advertising campaign. Unlike the deterministic model, which relies on direct evidence like a click or user ID, this model evaluates the likelihood that an event is linked to a particular source.
How It Works:
- Aggregated Data Collection: Analyzing global trends such as ad impressions, clicks, and temporal data.
- Statistical Computation: Using algorithmic models, such as Bayesian models or regression analysis, to estimate attribution probabilities.
- Outcome Prediction: These probabilities infer which campaign most likely contributed to an action, even without direct data.
This methodology relies on analyzing large data sets and correlations rather than explicit and unique links.
Nota Bene: MMPs (Marketing Measurement Partners) like Adjust or Appsflyer have developed their own attribution models.
Why Adopt the Probabilistic Model?
The shift to the probabilistic has been accelerated by several key factors:
1. Regulatory Changes: With the end of IDFA and regulations like GDPR and CCPA, marketers lost much of their ability to precisely track users. The industry turned to privacy-compliant models that avoid directly collecting or using personal data.
2. Need for Large-Scale Optimization: Modern advertising campaigns operate across multiple channels (social, search, display, etc.). This model helps decode the combined performance of these efforts without requiring granular individual tracking.
3. Increasingly Complex User Journeys: Today, a user might see an ad on Instagram, click a Google ad, and ultimately install an app after an organic search. Probabilistic models identify key influences in these complex paths.
4. Technological Evolution: Attribution tools, including DSP platforms and MMPs like Adjust and AppsFlyer, increasingly integrate these kind of models, employing advanced techniques such as Bayesian analysis and machine learning algorithms.
5. Flexibility and Responsiveness: In a world where advertising trends evolve rapidly, the probabilistic model enables real-time campaign adjustments based on established probabilities rather than outdated or partial data.
6. Increased Focus on KPIs: Advertisers are seeking metrics that reflect overall performance rather than isolated indicators. The probabilistic model meets this need by offering a comprehensive view of campaign ROI.
This model bridges the gaps left by traditional solutions while complying with new privacy standards.
Pros & Cons of the Probabilistic Model
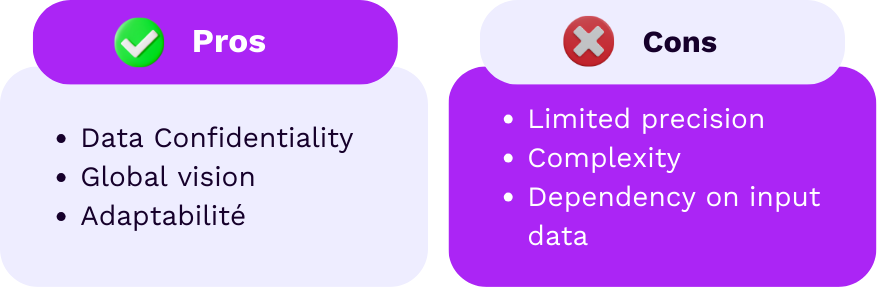
Advantages:
- Privacy-Friendly: It adapts seamlessly to environments with limited user data.
- Global Insights: Provides a comprehensive view of campaign impact without direct access to user data.
- Adaptability: Ideal for multi-source campaigns where data is fragmented.
Disadvantages:
- Limited Precision: Results are based on probabilities, introducing a margin of error.
- Complexity: Calculations and analyses require advanced data analysis skills.
- Dependence on Data Quality: Poor-quality data leads to poor results.
Probabilistic Model vs. Deterministic Model
The deterministic and probabilistic models are opposing but complementary approaches:
- Deterministic Model: Based on tangible evidence like a click or user ID. Extremely precise but heavily dependent on data availability.
- Probabilistic Model: Provides an estimation based on global data and patterns. Less precise but more suited to current data limitations.
Which Model to Choose? It depends on campaign objectives and constraints. In low-data-access environments, the probabilistic model is preferable.
Probabilistic Model vs. SKAN
What is SKAN?
SKAdNetwork (SKAN) is Apple’s attribution solution that provides aggregated and anonymous reports on campaign performance.
Key Differences:
- Data Granularity: SKAN offers highly aggregated information, whereas the probabilistic model can yield more precise insights using advanced algorithms.
- Complementarity: Combining both approaches allows marketers to benefit from Apple’s compliance standards and a broader global view.
To find out more, read our latest Acquisition Battle: SKAN vs Probabilistic Model

Do not hesitate to contact with our teams
Addict can support you to improve your performance.
Probabilistic Model Glossary
The probabilistic model connects to several key concepts from statistics, data science, and digital marketing:
- Multi-Touch Attribution (MTA): Assigns credit to multiple touchpoints in the customer journey instead of focusing solely on the last click.
- Statistical Regression Models: Predict a dependent variable (e.g., conversion) based on independent variables (e.g., impressions, clicks).
- Attribution Window: The attribution window refers to the time frame during which a conversion can be attributed to a specific interaction (e.g., click or impression).
- Correlation Analysis: Measures the strength and direction of relationships between two variables.
- Machine Learning and Predictive Algorithms: Train models to identify patterns and make predictions based on data.
- Cohort Analysis: Segments users into groups based on shared characteristics or behaviors (e.g., users who installed an app after seeing a specific ad).
- Data Anonymization and Privacy-by-Design: Practices ensuring user data protection by anonymizing or minimizing collected information.
- Modeled ROI (Return on Investment): Estimates campaign profitability using partial data and statistical models.
Conclusion
In light of today’s challenges, the probabilistic model is emerging as a suitable and sustainable solution for understanding and optimizing advertising campaigns. By combining it with other approaches like SKAN, marketers can stay ahead in a rapidly evolving industry.


