First-Party Data: Definition, Challenges & Marketing Strategies
Introduction
In a digital landscape increasingly shaped by privacy regulations and the phasing out of third-party cookies, first-party data has become a critical asset for businesses. For app marketers, it offers both a competitive edge and a powerful performance driver.
What Is First-Party Data?
Definition
First-party data refers to information that a company collects directly from its users, customers, or prospects through its own channels—such as its website, mobile app, CRM, loyalty programs, customer service, etc.
These data are valuable because they are:
- Reliable (from a direct source)
- Personalized
- Compliant with regulations (GDPR, ATT…)
- Free to collect (compared to buying external data)
What Types of First-Party Data Exist?
CRM Data
- Demographic info (age, gender, location…)
- Contact info (email, phone number, address)
- Transaction data (purchase history, average basket, frequency)
- Life events (birthdays, personal milestones)
- Consent preferences (opt-in / opt-out)
- Loyalty program participation
- Customer service interactions
Behavioral Data
- Website or app browsing behavior
- Pages viewed
- Items added to cart
- Features used within an app
- User journey
Advertising Exposure Data
- Interaction with ads
- Click-through rates
- Video views
- Post-click engagement
How to Collect First-Party Data
First-party data is only valuable if collected efficiently and transparently. As users become increasingly sensitive to how their data is used, brands must ensure collection points are both relevant and valuable to the user.
Sign-up and Account Creation Forms
Still one of the most common ways to collect direct user data:
- Name
- Phone number
- Preferences
- Birth date
- Interests
Balance is key—longer forms risk higher abandonment rates.
Mobile Apps (In-App Events)
Apps offer rich behavioral data:
- Screens viewed
- Time spent
- Clicks
- User flows
- Features used
- Usage frequency
- In-app purchase history
These insights can be used to:
- Improve UX
- Personalize content
- Power retargeting and re-engagement campaigns
Social Logins
Letting users log in via platforms like Facebook, Google, or Apple helps collect verified and enriched data:
- Profile info
- Verified email
- Photos
- Interests
- Friend lists (with permission)
It’s quick, convenient, and often preferred by users.
Online and Offline Purchase History
Transactional data (what, when, how often, how much, payment method…) provides deep insight into customer behavior.
Cross-device data is possible if accounts are unified (e.g., in-store + mobile app).
Cookies & Tracking Pixels (where still allowed)
First-party cookies remain vital for tracking on-site/app behavior:
- Page views
- Journeys
- Cart abandonment
- Interests
Same goes for tracking pixels in emails or media campaigns.
User Feedback & Surveys
Asking users directly through surveys, satisfaction forms, or Net Promoter Score (NPS) provides valuable input:
- Issues faced
- Expectations
- Suggestions
- Interest in new products or features
It also shows that the brand listens.
Games, Contests, Quizzes
These fun and engaging formats are widely used in marketing to collect data:
- Name
- Product preferences
- Quiz score
- Purchase intent
As long as rules are clear and transparent about data usage.
Why Is First-Party Data Essential in App Marketing?
Here’s how first-party data fuels user acquisition and retention strategies:
Build Trust with Users
First-party data collection follows a clear value exchange: give to get.
In return for their data, users expect a better experience, personalized content, or relevant offers. To strengthen trust:
- Be transparent about data usage
- Offer clear benefits (exclusive content, promos, features)
- Provide easy control (opt-in / opt-out)
Trust is now a competitive advantage.
Enable Precise Segmentation
First-party data allows brands to build highly granular audience segments based on real user behavior:
- Demographics
- In-app behavior (features used, frequency, churn risk)
- Purchase history
- Marketing engagement (clicks, email opens, push interactions)
Better segmentation means more relevant messages hence better campaign performance (CRM, push, ads, emails…).
Personalize Messages & Offers
In the mobile space where attention is scarce, personalization is key. First-party data helps tailor:
- Push notifications
- In-app messages
- Commercial offers
- User journeys
Example: a user frequently browsing a product category may receive a targeted offer related to it.
Results: higher conversions, retention, and satisfaction.
Optimize Acquisition & Retention Campaigns
First-party data strengthens acquisition and re-engagement strategies through:
- Custom Audiences
- Lookalike campaigns
- Smarter retargeting
- Behavior-based messaging
In a post-ATT, post-cookie world, advertisers mastering their own data are less reliant on ad platforms.
Improve Product Through Behavior Insights
First-party data is not just for marketing—it’s a powerful analytics tool for product and UX teams:
- Identify app friction points
- Understand churn reasons
- Spot top features
- Refine user flows
- Prioritize product development
Better behavioral insight means better product hence sustainable growth.
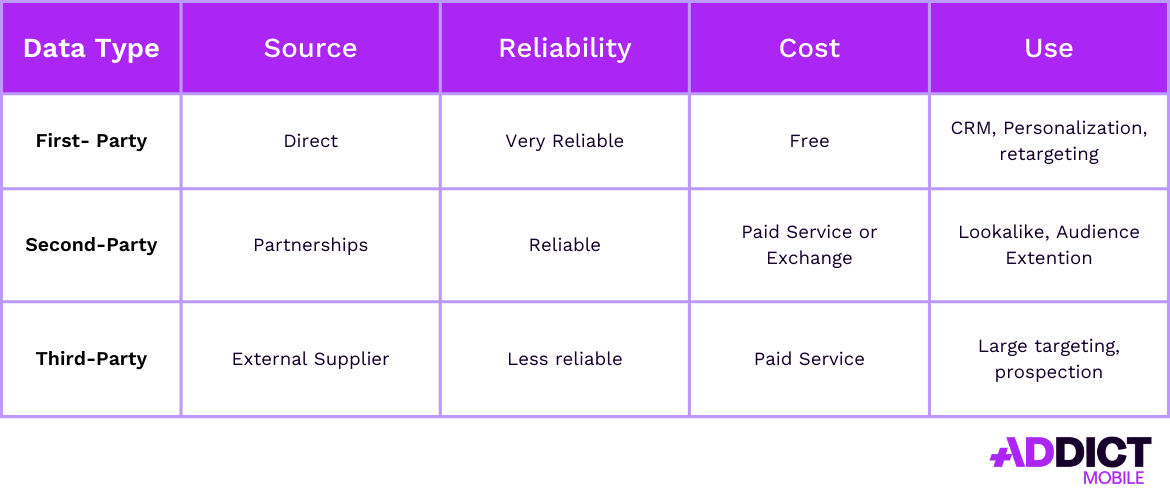
First-Party vs Second-Party vs Third-Party Data
1st Party vs 2nd Party
Second-party data is someone else’s first-party data shared through partnerships (e.g., brand collaborations).
1st Party vs 3rd Party
Third-party data is bought from external providers (e.g., programmatic audience databases).
Recap:
The End of Third-Party Cookies: What It Means for App Marketing
Impact #1 — More Contextual Campaigns, Less Reliance on Tracking
With fewer data signals, marketers must shift toward creative, context-based strategies. Ads should resonate based on context (location, time, device, content) instead of user profiles.
Impact #2 — Rise of “Logged-In” Environments
Big tech (Google, Meta, TikTok, Amazon) and app publishers with large logged-in user bases are becoming strategic. Why? Because they own their own first-party data and can still offer strong targeting.
Impact #3 — Attribution & Measurement Get Harder
The end of cookies and IDFA/GAID restrictions has changed marketing measurement:
- Rise of probabilistic attribution models
- Use of aggregated data (SKAdNetwork, Privacy Sandbox)
- Shift to macro KPIs (incrementality, cohorts, LTV)
- Need to combine multiple data sources
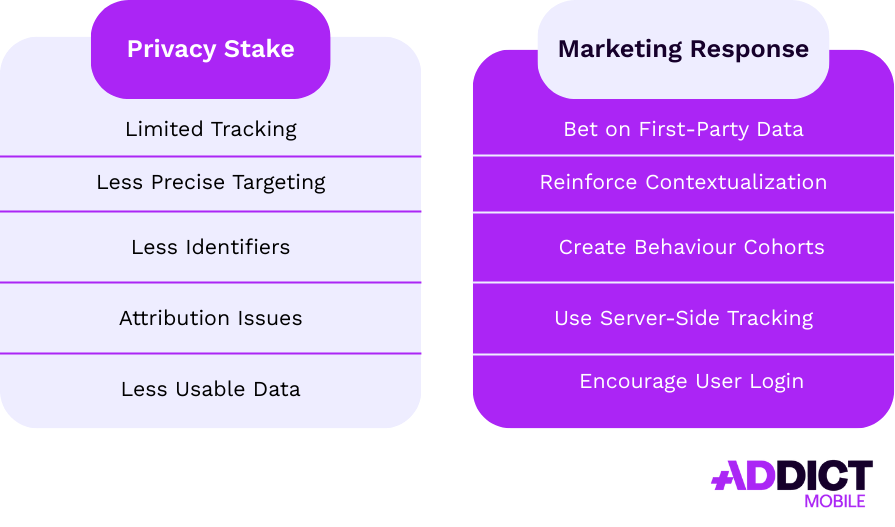
Navigating Google Privacy Sandbox & Apple’s ATT
Between Google’s Privacy Sandbox (Android) and Apple’s App Tracking Transparency (iOS), mobile marketers now operate in a world where individual tracking is limited or forbidden without consent. But there are still effective levers to pull.
Campaign Contextualization: The Right Message at the Right Time
As identity becomes blurred, placement context becomes key. Consider:
- The app/site where the ad is shown
- The content being viewed
- Time of day and location
- Device and OS
Example: an ad for a food delivery app shown at 7PM within a recipe app will have a high impact.
Leverage First-Party Signals: Use Your Own Data as a Growth Engine
With third-party signals fading, first-party data becomes essential to:
- Build lookalike audiences
- Power CRM campaigns (email, push, SMS)
- Personalize messages and offers
- Improve in-app targeting and scoring
Example: target a user who made a single purchase with a reactivation offer via server-side campaign.
Cohort-Based Strategies Instead of Hyper-Personalization
Cohorts group users based on shared behavior rather than identity.
Examples of useful cohorts:
- New signups
- Active users (last 7 days)
- Cart abandoners
- Premium vs. free users
- Inactive for 30+ days
These cohorts are great for engagement, upsell, and reactivation campaigns.
Login-first & Account-Based Marketing
Getting users to create accounts is now a strategic priority. Benefits include:
- Personalized onboarding
- Exclusive perks for logged-in users
- Easy social login (Google, Apple, Facebook)
- Members-only features
The more identified a user is, the more actionable their data becomes.
Optimize Server-Side Tracking
Server-side tracking is now essential to:
- Capture more in-app events
- Bypass browser and OS limitations
- Secure collected data
- Feed ad platforms and analytics tools
Example: sending conversions (installs, purchases, signups) via server-to-server APIs to Meta, Google, TikTok keeps signals reliable even without cookies or IDFA.des signaux fiables malgré les restrictions des cookies ou de l’IDFA.
To summarize

Do not hesitate to contact with our teams
Addict can support you to improve your performance.
Summary: How to Collect More First-Party Data
- Encourage account creation/login
- Offer content or benefits in exchange for data (gated content)
- Launch engaging loyalty programs
- Use incentives (discounts, games)
- Multiply touchpoints (email, push, in-app, SMS…)
- Leverage in-app analytics
Conclusion
In a world without third-party cookies and with rising privacy restrictions, first-party data is the foundation of successful and sustainable marketing strategies. Brands that invest early in collecting, structuring, and smartly using their own data will lead the way tomorrow.


